VBA provides many operators, which can be used to implement complex operations. Today, the author will share the basic operators and operations provided by VBA, and their basic usage.
VBA operators can be divided into the following 6 categories:
- Assignment operator
- Arithmetic Operator
- Comparison operator
- Logical Operators
- Concatenation operator
- Other operators
Assignment Operator
The first is the most basic, the assignment operator (= ). In the VBA variable article, the core of the assignment syntax is = (equal sign), the variable is on the left, and the data is on the right. It can be understood that the variable is equal to the assigned data.

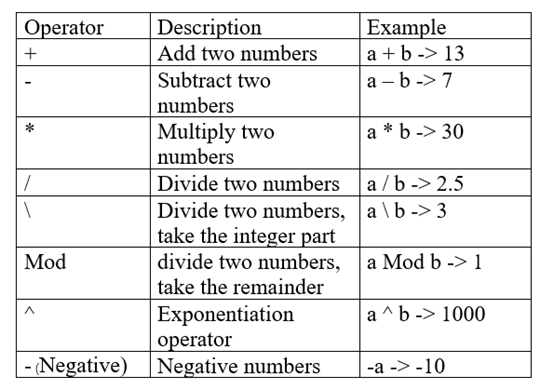
Arithmetic Operator
Arithmetic operators are commonly used mathematical operators, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The complete arithmetic operators in VBA are as follows.
Assuming a = 10, b = 3, -> means the result.
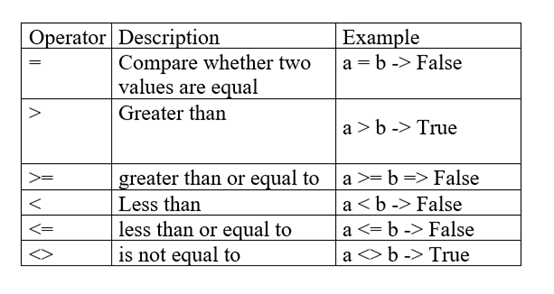
Comparison Operator
Comparison operator, this operator will compare the two variables provided, if the comparison conditions are met, it returns True, otherwise, it returns False.
Assuming a = 10, b = 3, -> means the result.
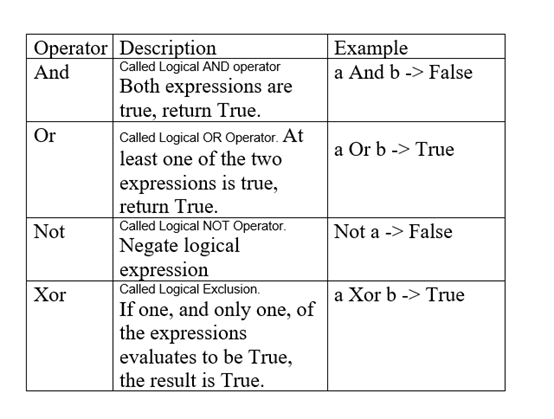
Logical Operators
Logical operators perform logical operations on logical values, namely True and False, and return the result of the operation, which is also a logical value.
Assuming a = True, b = False, -> means the result.
Concatenation Operator
The concatenation operator in VBA is used to concatenate two or more texts. Its usage is the same as the & symbol in Excel formulas.

Other Operators


Leave a Reply